Interdisciplinary BioMedical group on Artificial Intelligence
MULTIDISCIPLINARY BOARDS
A two-year long worldwide medical emergency has dramatically exacerbated inequalities that already existed before the Covid-19 pandemic. The IBMAI association - Interdisciplinary BioMedical group on Artificial Intelligence - was founded in 2022 to speak up against, and combat, inequalities in access to healthcare. IBMAI is an interdisciplinary research group composed of researchers from various scientific fields, ranging from medicine, biology, chemistry, engineering, computer science and electronics. This wide array of expertise gives us the opportunity to address high-impact issues in the field of health by applying innovative information technology, and to develop procedures using artificial intelligence to minimise the costs of various services provided by hospitals.
AIM
The aim of the IBMAI association is to bring every possible tool, including ultrasound diagnostics, telemedicine and all devices capable of using artificial intelligence, to areas where there are no suitable healthcare facilities, such as third world countries and war-torn areas, and to people who still live in discriminatory social and labour situations. Even without looking at the global scale this project may reach and limiting ourselves to the reality that surrounds us, we aim to help patients who may suffer from varying levels of social and medical discrimination, such as people of different ethnicity, religion and/or gender identity, the elderly, and patients with disabilities or chronic diseases that inevitably entail an inability to work, etc... In short, all human beings upon whom society looks with disfavour. The guarantee of healthcare services that are minimal but fundamental for the start of a good diagnostic process, provided by more specific and in-depth instrumental diagnostic examinations, should be a right for all. The realisation of our project, with its vast potential, has all the credentials to become reality and would lead to the acquisition of some of these diagnostic tools useful to save lives and furthermore improve them in the aforementioned places and situations. Particular emphasis will be placed on those individuals to whom medicine still represents a luxury, and whose healthcare system is a limitation rather than an opportunity. We would like to make healthcare democratic by making it accessible to all. To us, the dreamers, the potential of this mission seems enormous and presents innumerable applications: healthcare is a universal right... let us share and not divide!
OUR PROJECT
Increasingly technological medicine requires strong educational support and this is why IBMAI pays particular attention to the training of professionals with multidisciplinary skills, capable of independently using and managing advanced technologies in fields ranging from bioinformatics to medical robotics. We also must not neglect the fundamental aspects needed to inform both patient and doctor so as to provide the necessary healthcare services of the future.LAD-T PROJECT
We are developing a ’REDOX-LAB wearable sensor’ aimed at informing athletes, be they professional or amateur, about the best environment in which to train and the risks they might be exposed to when training in an inappropriate environment. The ultimate goal is to alert people in real time when oxidative stress nears predefined thresholds, so as not to turn a healthy habit into a risky activity. These thresholds will be customised for the individual.
EMOTIONAL ROBOT IN THE ER:
The use of robots in paediatric care is increasing but, until now, no successful interaction strategies have been proposed. We studied the emotional impact of robot use in a cohort of 700 children enrolled in the paediatric emergency department of the San Salvatore Hospital in L’Aquila.
TIME-DEPENDENT PATHOLOGIES: PDTA OPTIMISATION
Stroke is a medical emergency that leads to the onset of an acute neurological syndrome with symptoms persisting for upwards of 24 hours. Neuronal loss during an ischaemic event is equivalent to 1 million neurons per minute: early diagnosis and intervention therefore play a key role. Our study aims to improve and shorten the time taken to activate therapeutic and diagnostic procedures in the emergency room.
ARTIFICIAL IINTELLIGENCE AT THE PHYSICIAN’S SERVICE:
In order to support emergency room physicians in managing the SARS-CoV2 pandemic, we created a predictive model based on machine learning techniques for the safe discharge of patients from the ER. From the15 th of April 2020 to the15 th of February 2021, we monitored a cohort of 779 patients at three hospitals in the regions of Lazio and Abruzzo. Our prediction model demonstrated an accuracy of 86% for safe discharge, with specificity of 35% and sensitivity of 97%. The model was integrated into an APP to support the physician in the ER.
Our Team

FOUNDING MEMBERS:
Clara Balsano - University of l’Aquila
Bruno Siciliano - University of Napoli Federico II
Silvano Jr Santini - University of l’Aquila
MAKE A DONATION
HEALTH IS DEMOCRATIC, WE SHARE AND NOT DIVIDE!.
Scolarships
News
April 22, 2024 April 14, 2024 March 28, 2024 March 14, 2024 Informazione Quotidiana - May 5, 2023 Vimeo - May 20, 2023Laboratorio SIMULAQ for trainees of the Emergency Medicine Specialization School
Award for Medicine to Professor Clara Balsano
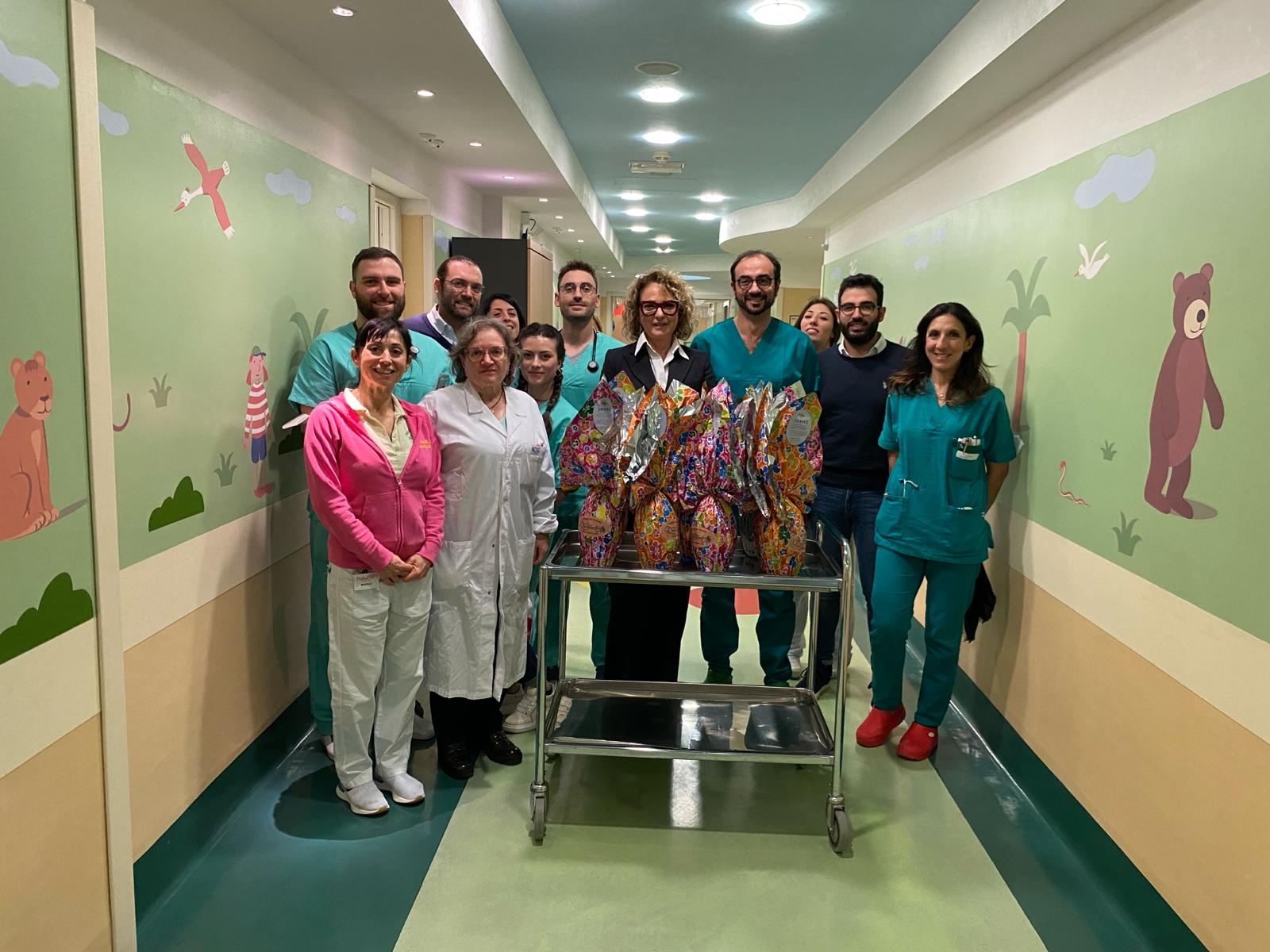
Easter Egg Donation to the Pediatric Emergency Department of L'Aquila

Theatrical-Musical Show

Liver disease is an alarm: in the next 10 years + 50% of cases of cirrhosis and + 100% of hepatocellular carcinomas are estimated. For the PreDEA study presented in L’Aquila, the data on fatty liver disease are underestimated.
It takes guts for research and progress.
 Coming soon... Online Course on Mobile App Creation for EULiST Student - Reserve a spot by sending an email to
Coming soon... Online Course on Mobile App Creation for EULiST Student - Reserve a spot by sending an email to




